Usm observer EN: различия между версиями
Нет описания правки |
Нет описания правки |
||
| (не показаны 2 промежуточные версии этого же участника) | |||
| Строка 3: | Строка 3: | ||
{{ActivEN}} | {{ActivEN}} | ||
'''usm_observer''' - is a module for constant control by SNMP means of configurable indicators of [[Equipment|devices]] and notification of [[ | '''usm_observer''' - is a module for constant control by SNMP means of configurable indicators of [[Equipment|devices]] and notification of [[Staff|staff]] and [[Subdivisions|subdivisions]] about the fact of these indicators' values exceeding the set values. | ||
| Строка 19: | Строка 19: | ||
''The module requires Python3 of any currently supported version. The status of versions can be viewed here:"[https://devguide.python.org/versions/ Status of Python versions]". It is recommended to use a version with "security" or "bugfix" status. Versions marked as "end-of-life" are not supported. Versions marked as "feature" are not recommended.'' | ''The module requires Python3 of any currently supported version. The status of versions can be viewed here:"[https://devguide.python.org/versions/ Status of Python versions]". It is recommended to use a version with "security" or "bugfix" status. Versions marked as "end-of-life" are not supported. Versions marked as "feature" are not recommended.'' | ||
=== Installation === | |||
Copy the archive to the modules directory, e.g. /opt/userside and unzip it. | |||
<pre> | |||
cd /opt/userside | |||
sudo unzip usm_observer_2.0.0.zip | |||
</pre> | |||
Navigate to the usm_observer directory, create a virtual environment | |||
<pre> | |||
cd usm_observer | |||
sudo python3 -m venv venv | |||
sudo venv/bin/pip install --upgrade pip | |||
sudo venv/bin/pip install --upgrade -r requirements.txt | |||
</pre> | |||
== | === Setting === | ||
If this is the first setting of version 2.x, copy the example configuration file | |||
<pre> | |||
sudo cp settings.yaml-example settings.yaml | |||
</pre> | |||
Edit the settings.yaml file. In the '''api''' section, specify <code>url</code> of your USERSIDE and [[UserSide API Key EN|API-key]] in the field <code>key</code>. In the '''log''' section you can change the path to the logs in the field <code>path</code> and the logging level (DEBUG, INFO, WARNING, ERROR) in the field <code>level</code>. If you want the log to be output to standard output instead of a file, then for <code>path</code> specify the value <code>STDOUT</code> — this may be useful when initially setting up the module. | |||
== Test launch == | == Test launch == | ||
To | To make it easier to control the first test launch, set the path to the log in settings.yaml to <code>STDOUT</code> and launch the module: | ||
<pre> | |||
venv/bin/python main.py | |||
</pre> | |||
If the module worked correctly and terminated correctly, set | If the module worked correctly and terminated correctly, set the correct path to the log so that it is recorded to a file. | ||
If errors were detected during the manual test launch, eliminate them or contact our support | If errors were detected during the manual test launch, eliminate them or contact our support team using the ticket system in your personal account. | ||
== Automatic | == Automatic start == | ||
Add a line to crontab, having previously changed the path to the module: | Add a line to crontab, having previously changed the path to the module: | ||
<pre> | |||
2/* * * * * root /opt/userside/usm_observer/venv/bin/python /opt/userside/usm_observer/main.py | |||
</pre> | |||
Make sure that the module starts. To do this, observe the log file after a few minutes: | |||
<pre> | |||
Make sure that the module starts. To do this, observe the log file after | tail -f /var/log/usm_observer/usm_observer.log | ||
</pre> | |||
== Rotation of log files == | |||
The log files created by the module need to be rotated. For this purpose, the standard log rotation tools in the operating system should be used. | |||
The following configuration will rotate all *.log files on a daily basis and store 7 archive copies (for 7 days) | |||
Create the following file /etc/logrotate.d/usm_observer: | |||
<pre> | |||
/var/log/usm_observer/usm_observer.log { | |||
rotate 7 | |||
daily | |||
compress | |||
delaycompress | |||
missingok | |||
notifempty | |||
} | |||
</pre> | |||
== Operation Logic == | == Operation Logic == | ||
Текущая версия от 09:00, 3 февраля 2025
|
This function is one of the possibilities |
usm_observer - is a module for constant control by SNMP means of configurable indicators of devices and notification of staff and subdivisions about the fact of these indicators' values exceeding the set values.
This module is a replacement for the obsolete us_control_EN module
Overview
Module Language: Python
Current version: see page: Modules_EN
Module Status: Paid
The module requires Python3 of any currently supported version. The status of versions can be viewed here:"Status of Python versions". It is recommended to use a version with "security" or "bugfix" status. Versions marked as "end-of-life" are not supported. Versions marked as "feature" are not recommended.
Installation
Copy the archive to the modules directory, e.g. /opt/userside and unzip it.
cd /opt/userside sudo unzip usm_observer_2.0.0.zip
Navigate to the usm_observer directory, create a virtual environment
cd usm_observer sudo python3 -m venv venv sudo venv/bin/pip install --upgrade pip sudo venv/bin/pip install --upgrade -r requirements.txt
Setting
If this is the first setting of version 2.x, copy the example configuration file
sudo cp settings.yaml-example settings.yaml
Edit the settings.yaml file. In the api section, specify url of your USERSIDE and API-key in the field key. In the log section you can change the path to the logs in the field path and the logging level (DEBUG, INFO, WARNING, ERROR) in the field level. If you want the log to be output to standard output instead of a file, then for path specify the value STDOUT — this may be useful when initially setting up the module.
Test launch
To make it easier to control the first test launch, set the path to the log in settings.yaml to STDOUT and launch the module:
venv/bin/python main.py
If the module worked correctly and terminated correctly, set the correct path to the log so that it is recorded to a file.
If errors were detected during the manual test launch, eliminate them or contact our support team using the ticket system in your personal account.
Automatic start
Add a line to crontab, having previously changed the path to the module:
2/* * * * * root /opt/userside/usm_observer/venv/bin/python /opt/userside/usm_observer/main.py
Make sure that the module starts. To do this, observe the log file after a few minutes:
tail -f /var/log/usm_observer/usm_observer.log
Rotation of log files
The log files created by the module need to be rotated. For this purpose, the standard log rotation tools in the operating system should be used.
The following configuration will rotate all *.log files on a daily basis and store 7 archive copies (for 7 days)
Create the following file /etc/logrotate.d/usm_observer:
/var/log/usm_observer/usm_observer.log {
rotate 7
daily
compress
delaycompress
missingok
notifempty
}
Operation Logic
- Each launch the module checks the status of SNMP-parameters of the monitored devices. If the value of a parameter is out of limits, an alarm is considered to have occurred. There can be several alarm parameters on a device. For each device, where an alarming parameter was found or vice versa - the parameter came back to normal - an e-mail and/or SMS is generated for the selected (at the level of each device) circle of recipients
- A separate e-mail/message is generated for each device, which will contain all the parameters whose (alarm/normal) status has changed. The information will be presented in the letter in a detailed manner, and in SMS in a compact manner
- The next message will be sent only if a parameter has changed again
- If during the polling process it is found out that the device being polled is inactive (an error occurred while connecting to the device or an error occurred during parameter acquisition), this will be marked by the module and in the next several startup cycles (default: 5) this device will not be polled, so as not to create delays in polling other parameters.
- For devices from which parameters were retrieved, the date of the last activity will be updated.
- If an invalid parameter (OID) is specified, when polling a device, polling of this device will be stopped on this parameter.
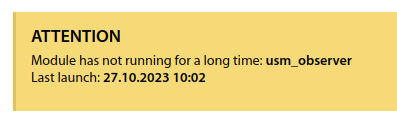
If the module has stopped starting - a corresponding message will be displayed on the main page for the operators having access to the system configuration
General Setup
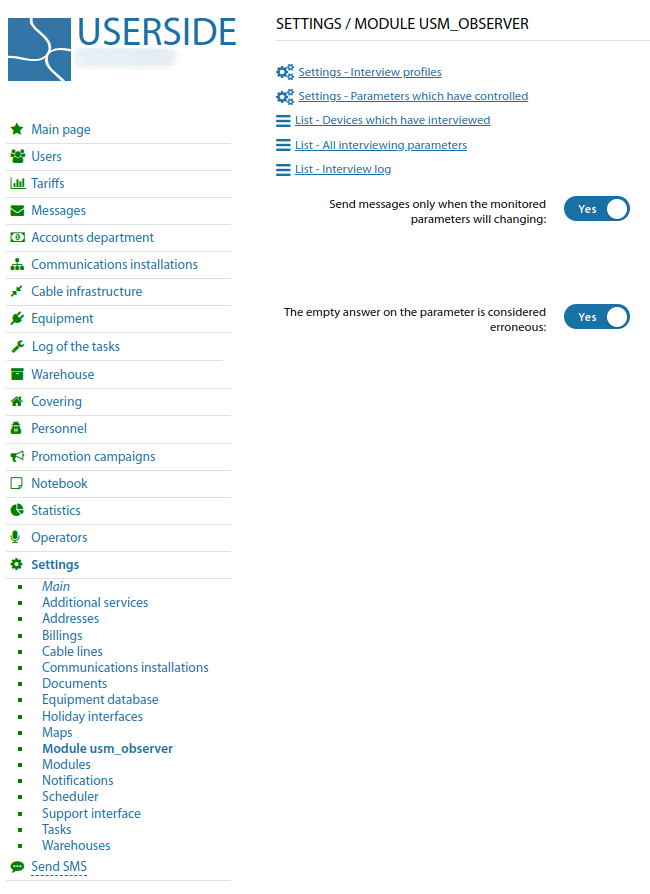
First, you need to specify a list of monitored parameters and the events at which to consider the values of these parameters to be out of normal.
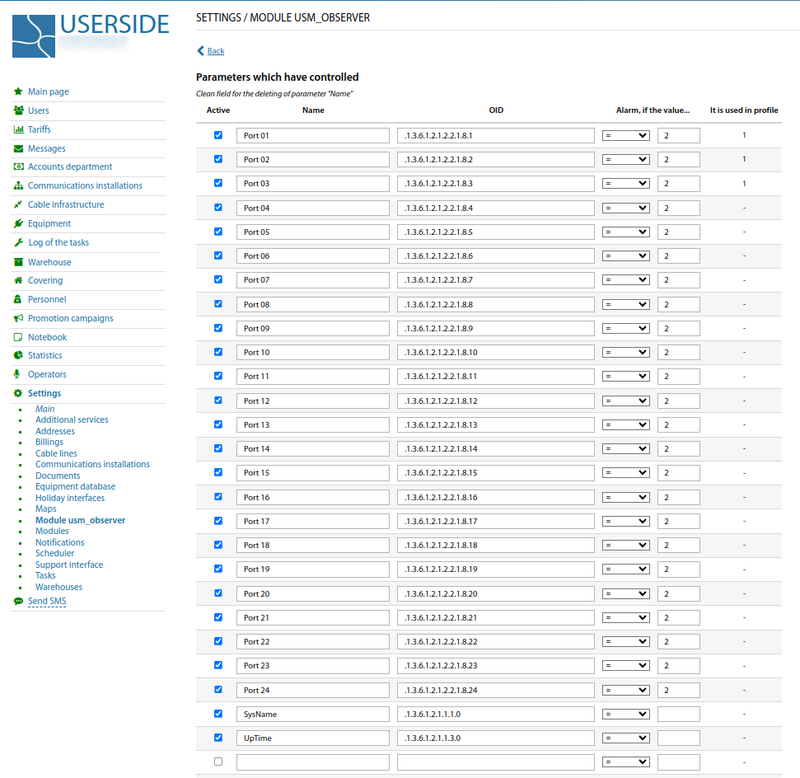
Parameters can be compiled into polling profiles
For all parameters that are currently being polled, the current status and alarms can be viewed
There is a log of polled parameters (not all values, only their changes), which is stored in the system database.
The current list of polled devices is also available
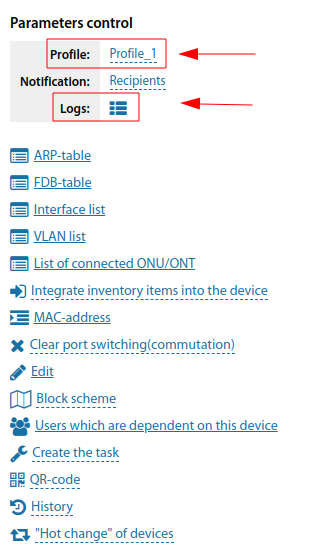
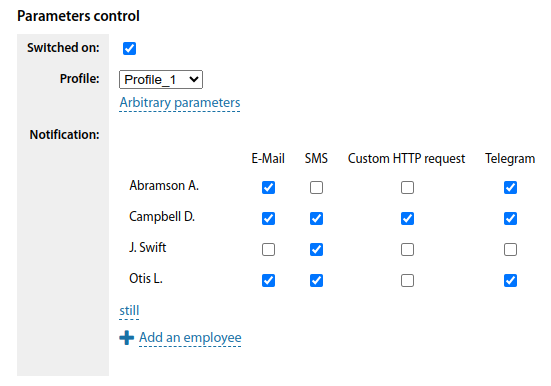
Customisation in the device card
When editing the equipment card, a block is available where you can select a polling profile for this device, specify some individual parameters for polling that are not included in the selected profile, and specify the recipients of alarm messages
In the view mode, the module block is also displayed and from it you can view the current state of the parameters and the log of their state changes